Introduction of NAPS;-
The National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS) is a flagship initiative of the Government of India aimed at promoting apprenticeship training and skill development across various sectors. Through financial incentives, industry partnerships, and skill training programs, NAPS seeks to bridge the gap between demand and supply of skilled workforce, thereby contributing to India’s economic growth and development.
Objectives of NAPS

In today’s rapidly evolving job market, the need for skilled workers is more pronounced than ever before. Recognizing this imperative, the Government of India introduced the National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS) with the aim of revolutionizing skill development and employment generation across various sectors. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the key objectives of NAPS and how they are shaping the future of India’s workforce.
Bridging the Skill Gap
One of the primary objectives of NAPS is to bridge the gap between the demand and supply of skilled workforce in the country. By providing structured apprenticeship programs, NAPS seeks to equip individuals with industry-relevant skills and competencies, thereby enhancing their employability and meeting the evolving needs of the job market.
Promoting Industry Engagement

NAPS aims to foster greater collaboration between industry stakeholders and training providers to ensure that apprenticeship programs are aligned with the needs of the industry. By actively involving employers in the training process, NAPS facilitates the creation of a job-ready workforce tailored to the specific requirements of different sectors.
Facilitating Employment Opportunities
At its core, NAPS is focused on creating meaningful employment opportunities for youth by offering them avenues for skill development and on-the-job training. By incentivizing employers to engage apprentices, the scheme not only addresses the issue of unemployment but also lays the foundation for sustainable economic growth.
Empowering Youth
Another key objective of NAPS is to empower the youth of India by providing them with access to quality education and training opportunities. Through apprenticeship programs, young individuals can gain hands-on experience, acquire new skills, and unlock their full potential, setting them on the path to a brighter future.
Enhancing Productivity and Competitiveness
By investing in skill development initiatives, NAPS aims to enhance the productivity and competitiveness of Indian industries. Skilled workers are more efficient, adaptable, and innovative, enabling businesses to stay ahead of the curve in an increasingly competitive global market.
Promoting Inclusive Growth
NAPS is designed to promote inclusive growth by ensuring that individuals from all sections of society have equal access to skill development opportunities. By reaching out to marginalized communities and underprivileged groups, the scheme aims to create a more inclusive and equitable society.
Strengthening the Economy
Ultimately, the overarching objective of NAPS is to strengthen the Indian economy by creating a skilled workforce that drives growth, innovation, and prosperity. By investing in human capital development, NAPS lays the foundation for a sustainable and resilient economy that can withstand the challenges of the future.
Key Components of NAPS
One of the central components of NAPS is the provision of financial incentives for employers who engage apprentices in their organizations. These incentives help offset the cost of training and encourage greater participation from the industry. Additionally, NAPS focuses on providing skill training to apprentices through designated training centers and industry partners, ensuring that they acquire relevant competencies for the job market.
Implementation of NAPS
The National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS) stands as a cornerstone in India’s endeavor to revolutionize its workforce and skill development landscape. Initiated by the Government of India, NAPS aims to bridge the gap between industry demands and skill availability by promoting apprenticeship programs across diverse sectors. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of NAPS, its objectives, key components, implementation strategies, impact, and future outlook.
Impact of NAPS
The National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS) has made significant strides in transforming India’s skill development landscape and empowering its workforce. Let’s delve deeper into the impact of NAPS across various dimensions:
Increased Employment Opportunities:
NAPS has played a pivotal role in creating avenues for employment by bridging the gap between skill supply and demand. By providing structured apprenticeship programs, the scheme has facilitated the entry of youth into the workforce, especially in sectors facing skill shortages.
Skill Enhancement among Youth:
Through its comprehensive training modules, NAPS has empowered youth with industry-relevant skills, making them more employable and adaptable to changing market dynamics. Apprentices undergo hands-on training and gain exposure to real-world work environments, enhancing their practical knowledge and competencies.
Boost to Manufacturing and Service Sectors:
NAPS has fueled growth in key sectors such as manufacturing, construction, healthcare, information technology, and hospitality by ensuring a steady supply of skilled manpower. Industries benefit from the infusion of fresh talent, leading to increased productivity, efficiency, and innovation.
Contribution to Economic Growth:
The success of NAPS is intertwined with India’s economic progress. By equipping individuals with market-driven skills, the scheme drives productivity gains, fosters entrepreneurship, and stimulates economic activity. A skilled workforce fuels innovation and competitiveness, positioning India as a global leader in various industries.
In essence, NAPS has emerged as a catalyst for socio-economic transformation, empowering individuals, industries, and the nation as a whole. Through its multifaceted approach to skill development and employment generation, the scheme continues to shape India’s future by nurturing a skilled and inclusive workforce.
Challenges and Limitations
The National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS) has been instrumental in promoting skill development and enhancing employment opportunities in India. However, like any ambitious program, NAPS also faces several challenges and limitations that need to be addressed for its effective implementation and sustained impact.
Lack of Awareness: One of the primary challenges faced by NAPS is the lack of awareness among potential beneficiaries, including youth and employers. Many individuals are unaware of the benefits of apprenticeship programs and the opportunities available under NAPS. This lack of awareness often leads to low participation rates and underutilization of the scheme.
Quality of Training Programs: While NAPS aims to provide skill training to apprentices, the quality of training programs offered by various training providers and industry partners remains a concern. In some cases, the training may not be aligned with industry requirements or may lack practical relevance, leading to a gap between skills acquired and skills demanded by employers.
Industry Participation: Another challenge faced by NAPS is the limited participation of industries, especially small and medium enterprises (SMEs), in offering apprenticeship opportunities. Many SMEs may lack the resources or infrastructure to effectively engage in apprenticeship programs, thereby limiting the scope of the scheme.
Monitoring and Evaluation Issues: Ensuring the quality and effectiveness of apprenticeship programs under NAPS requires robust monitoring and evaluation mechanisms. However, there may be challenges in monitoring the progress of apprentices, assessing their performance, and maintaining accountability among training providers and employers.
Mismatch of Skills and Demand: NAPS aims to bridge the gap between the demand for a skilled workforce and the availability of skilled individuals. However, there may be instances where the skills acquired by apprentices do not match the demand of the industry, leading to underemployment or mismatches in the labor market.
Addressing these challenges and limitations requires concerted efforts from all stakeholders, including the government, industry associations, training providers, and educational institutions. Strategies such as enhancing awareness through outreach programs, improving the quality of training through curriculum reforms and industry collaborations, incentivizing industry participation, strengthening monitoring and evaluation mechanisms, and aligning skill training with industry demand can help overcome these challenges and maximize the impact of NAPS on India’s skill development landscape.
Success Stories
Ramesh’s Journey from Unemployment to Entrepreneurship
Ramesh, a young graduate from a rural village in Karnataka, struggled to find employment opportunities in his hometown. However, his life took a turn when he learned about NAPS through a local awareness campaign. He enrolled in an apprenticeship program offered by a nearby manufacturing company, where he gained hands-on experience in machine operation and maintenance. After completing his apprenticeship, Ramesh decided to start his own small-scale manufacturing unit, leveraging the skills and knowledge acquired during his training. Today, Ramesh’s business not only employs several individuals from his village but also contributes to the local economy.
Priya’s Transformation from School Dropout to Skilled Healthcare Professional
Priya, a young girl from a disadvantaged community in Bihar, dropped out of school due to financial constraints. Determined to support her family, she sought opportunities for skill development and employment. Through NAPS, Priya enrolled in an apprenticeship program at a local hospital, where she received training in patient care, medical assistance, and emergency response. The hands-on experience and mentorship provided during her apprenticeship helped Priya develop confidence and competence in her chosen field. Upon completing her training, Priya secured a full-time job as a certified healthcare assistant, enabling her to support her family financially and pursue her dreams of further education.
Suresh’s Success Story in the IT Sector
Suresh, a college dropout from Chennai, was passionate about technology but lacked formal education and employment opportunities. Despite facing numerous challenges, he was determined to build a career in the IT sector. Through NAPS, Suresh enrolled in an apprenticeship program with a leading software development company, where he received training in programming languages, software development methodologies, and project management. His dedication and hard work impressed his mentors, who offered him a permanent position upon completing his apprenticeship. Today, Suresh works as a software engineer, contributing to cutting-edge projects and inspiring other aspiring technologists with his journey from adversity to success.
These success stories demonstrate the transformative impact of NAPS in empowering individuals with skills, knowledge, and opportunities for personal and professional growth. By providing access to quality apprenticeship programs, NAPS not only enhances employability but also fosters entrepreneurship, socio-economic development, and inclusive growth across diverse communities in India.
Future Outlook and Expansion Plans
As we navigate through the ever-changing landscape of business, it becomes imperative to chart our course with foresight and strategic planning. In this article, we delve into the future outlook and expansion plans of our organization, outlining our vision for growth and development in the years to come.
Vision Statement
Our vision is to emerge as a global leader in our industry, setting new benchmarks for innovation, excellence, and sustainability. We aim to create value for all stakeholders while contributing positively to society and the environment.
Market Analysis
A comprehensive analysis of market trends and dynamics reveals promising opportunities for expansion and diversification. By leveraging emerging technologies and tapping into new markets, we can capitalize on untapped potential and stay ahead of the curve.

Strategic Goals
Our strategic goals encompass a wide range of objectives, including but not limited to:
1. Geographic Expansion
Expanding our presence into new geographic regions and international markets to reach a broader customer base and unlock new growth opportunities.
2. Product Diversification
Diversifying our product portfolio to cater to evolving customer needs and preferences, thereby enhancing our competitiveness and market relevance.
3. Digital Transformation
Embracing digital transformation initiatives to streamline operations, enhance customer experience, and drive efficiency and productivity across the organization.
4. Innovation and R&D
Continuously investing in research and development to foster innovation, create differentiated offerings, and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
5. Sustainable Practices
Embedding sustainability into our core business practices, including responsible sourcing, waste reduction, and carbon footprint mitigation, to contribute to environmental stewardship and social responsibility.
Expansion Strategies
To realize our strategic goals, we have devised a multifaceted approach that encompasses the following strategies:
1. Market Segmentation
Identifying and targeting specific market segments with tailored products and services to maximize customer satisfaction and market penetration.
2. Strategic Partnerships
Forging strategic partnerships and collaborations with industry peers, technology providers, and other stakeholders to enhance capabilities, access new markets, and drive innovation.
3. Customer-centric Approach
Adopting a customer-centric approach by actively listening to customer feedback, anticipating their needs, and delivering value-added solutions that exceed their expectations.
4. Talent Development
Investing in talent development initiatives to nurture a skilled and motivated workforce capable of driving organizational growth and innovation.
5. Agile Decision-making
Fostering a culture of agility and adaptability, enabling swift decision-making and course correction in response to changing market conditions and emerging opportunities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, NAPS stands as a testament to India’s commitment to fostering skill development and employment generation. By providing a platform for youth to acquire industry-relevant skills and gain practical experience, NAPS is not just empowering individuals but also driving economic growth and innovation. As the scheme continues to evolve and expand, it holds the promise of transforming India’s workforce and positioning the country as a global leader in skilled manpower.

FAQs
What are the eligibility criteria for participating in NAPS?
Eligibility criteria for NAPS vary depending on the specific apprenticeship program and industry sector. Generally, individuals between the ages of 18 to 35 years who have completed their basic education are eligible to apply for apprenticeship training.
How can employers benefit from enrolling in NAPS?
Employers can benefit from enrolling in NAPS by accessing a pool of skilled apprentices who can contribute to their organization’s productivity and growth. Additionally, participating employers are eligible to receive financial incentives and tax benefits under the scheme.
Are apprenticeship programs available in all sectors?
Yes, apprenticeship programs under NAPS are available across various sectors, including manufacturing, healthcare, information technology, construction, hospitality, and more. The scheme aims to cover a wide range of industries to cater to the diverse skill requirements of the economy.
How is the performance of apprentices monitored under NAPS?
The performance of apprentices enrolled in NAPS is monitored through regular assessments conducted by training providers and industry partners. These assessments evaluate apprentices’ progress, competency levels, and adherence to training objectives, ensuring quality and accountability.
What support is available for apprentices transitioning to full-time employment?
NAPS provides support to apprentices transitioning to full-time employment through career counseling, job placement assistance, and skill upgrade programs. Additionally, employers may offer apprenticeship completion certificates and on-the-job training opportunities to facilitate their integration into the workforce.
what is skill India?
Skill India is an initiative launched by the Government of India aimed at empowering the country’s workforce with relevant skills to enhance their employability and productivity. It focuses on providing training and certification programs across various sectors to bridge the gap between the demand for skilled labor and the availability of skilled manpower. The objective is to create a skilled workforce that meets the needs of India’s growing economy and promotes economic growth, entrepreneurship, and innovation.
RERA stands for Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act. It is a regulatory framework established by the Government of India to protect the interests of homebuyers and promote transparency and accountability in the real estate sector. RERA aims to regulate the real estate market by mandating registration of real estate projects and agents, ensuring timely delivery of projects, and preventing fraudulent practices. It also establishes regulatory authorities in each state to oversee the implementation of the Act and address grievances of homebuyers. RERA seeks to bring about greater transparency, professionalism, and efficiency in the real estate industry.
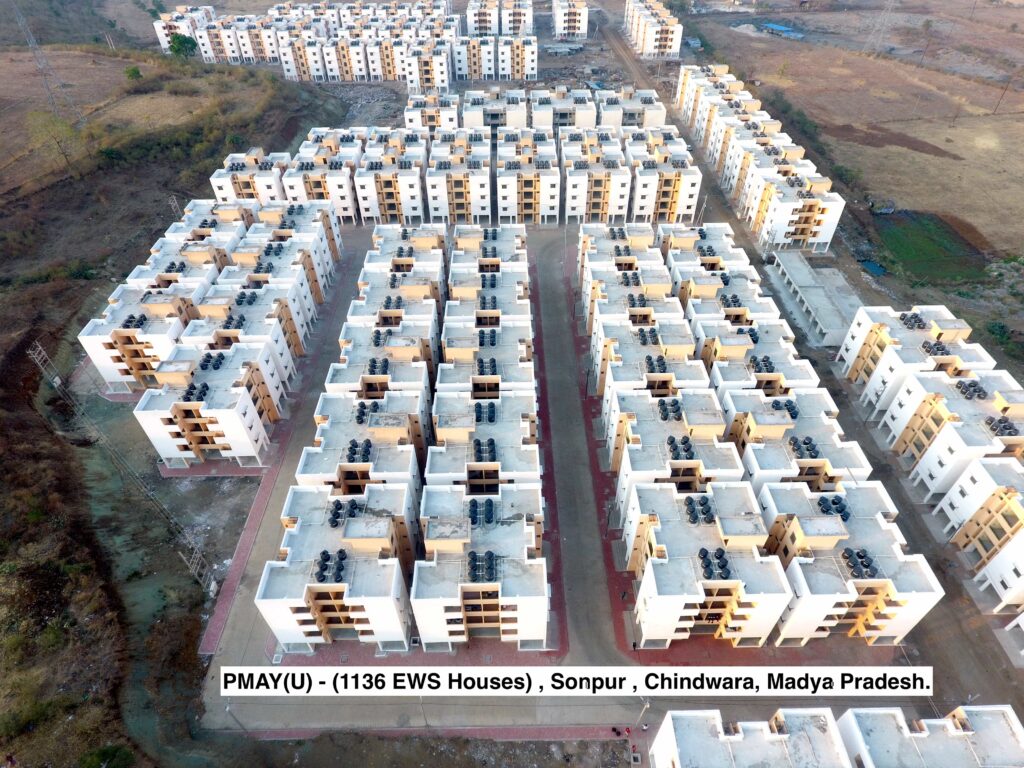
what is PMAY?
PMAY stands for Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana, which is a flagship affordable housing scheme launched by the Government of India. The aim of PMAY is to provide affordable housing to all eligible beneficiaries by the year 2022. It targets economically weaker sections (EWS), low-income groups (LIG), and middle-income groups (MIG) in both urban and rural areas. PMAY offers financial assistance through credit-linked subsidies, beneficiary-led construction, and affordable housing projects to enable eligible individuals to own a house. The scheme also focuses on promoting sustainable and inclusive urban development by providing infrastructure facilities in housing colonies.